Reader Bonus:
Challenger Hiring Guide

Across industries and around the world, sales organizations struggle to hire sellers equipped for an increasingly complex sales environment. In fact, as research in “The Challenger Sale” revealed nearly a decade ago, some competencies – relationship acumen and a “customer is always right” mentality, for instance – that traditionally differentiated star performers from their peers simply do not work in complex sales.
To thrive in this new environment, hiring managers must look for a new kind of seller: the Challenger. Far and away, this profile outperforms the rest. These sellers aren’t just meeting their quotas but consistently exceeding them, even in a difficult economy.
Who is the Challenger seller?
Someone who can…
- Teach customers unique insights about how to best compete in the marketplace
- Tailor messaging to each decision-maker across the customer organization
- Take control throughout the sales interaction to overcome customer risk aversion
- Deploy Constructive Tension across the sale to move customers toward consensus
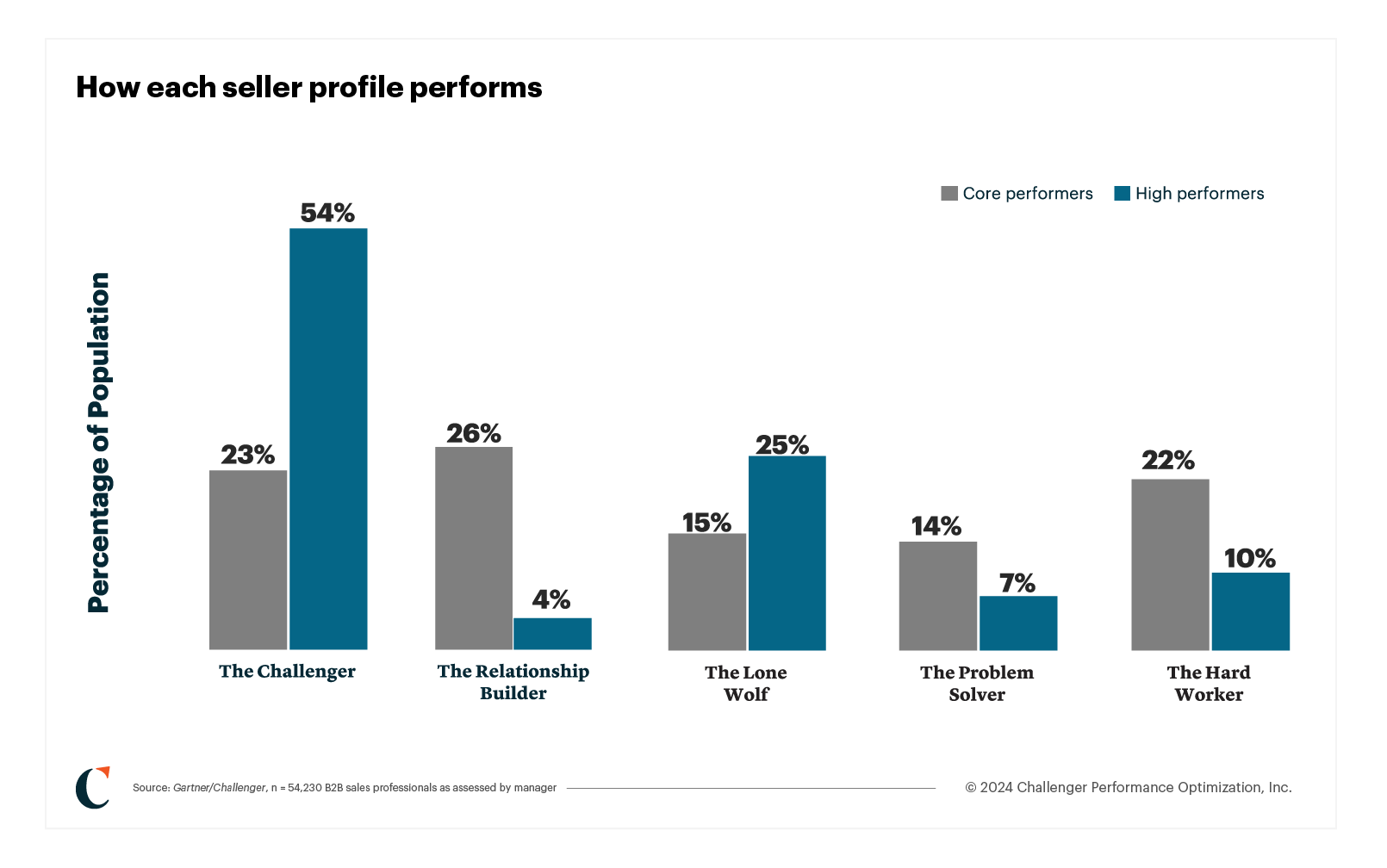
Why should you hire Challengers?
Because Challengers win. Challengers make up 39% of all high performers, higher than any other single profile. In contrast, only 7% of high performers come from the Relationship Builder profile. Challenger sellers exhibit a particular set of skills and behaviors that customers value. Counterintuitively, that’s why they outperform Relationship Builders: they aren’t afraid to challenge assumptions and offer new insights.
What competencies set Challengers apart?
Anyone used to hiring Relationship Builders or Hard Workers might ask: “How can I begin hiring for the most successful selling profile when it differs so significantly from other candidate profiles?”
To start, know that Challengers stand out for their ability to build Constructive Tension across customer interactions and across the sale. These interactions push the customer out of their comfort zone to teach them something new. They also stand out for their ability to:
- Offer unique perspectives
- Practice two-way communication
- Know their customers’ value drivers
- Identify economic drivers
- Get comfortable discussing money
- Pressure the customer
Here’s how those skills break down across the skills of Teaching, Tailoring, and Taking Control.
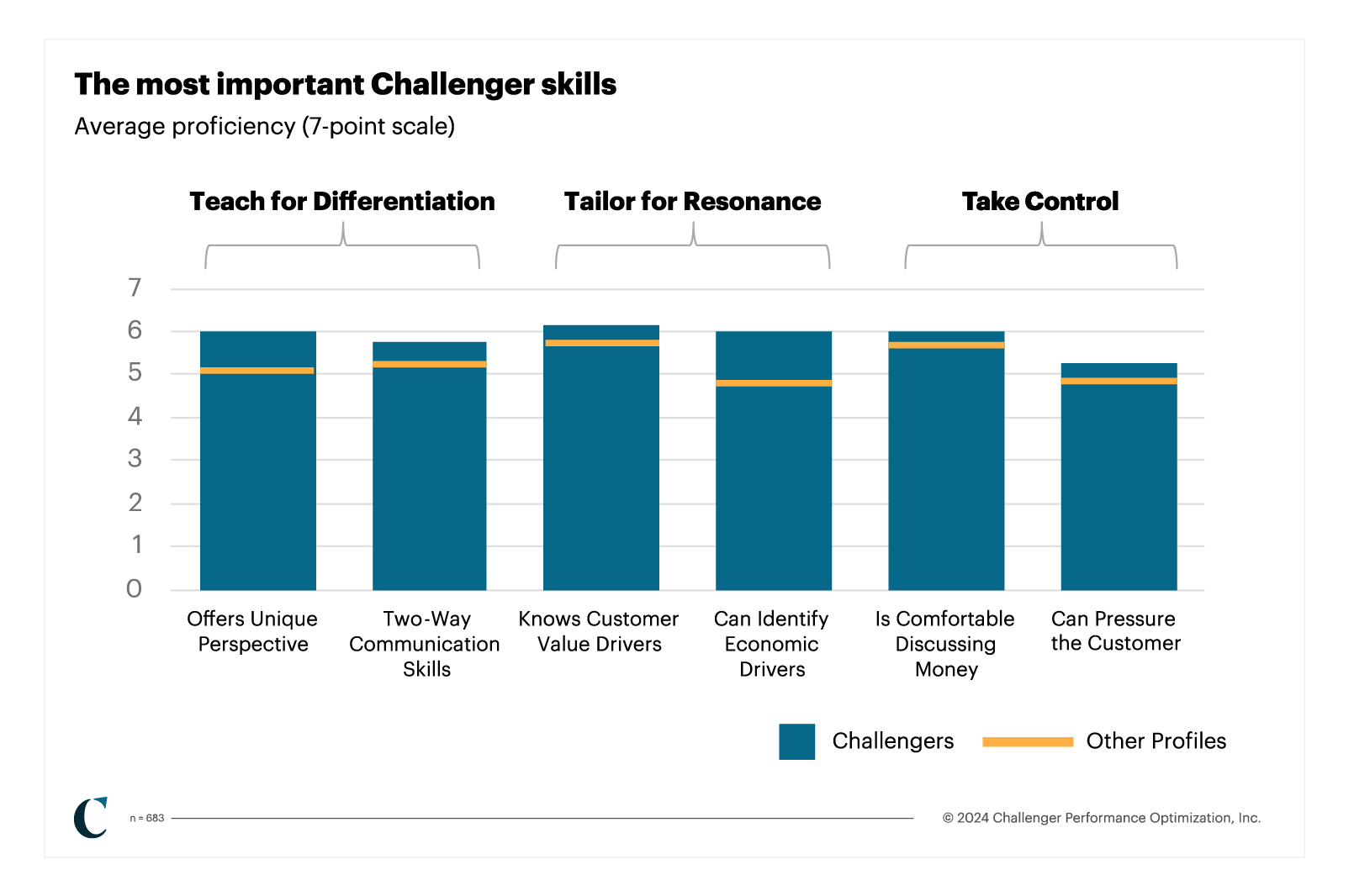
The Challenger hiring guide
Use the interview guide to identify, select, and hire Challenger sellers who meet these specific competencies.
Competency: Offers unique perspective
Definition:
- Reframes and challenges the way customers view their businesses.
- Aligns insights to key customer priorities and ties those insights back to the suppliers’ unique differentiators
Sample interview questions:
- How do you usually open a sales conversation?
- Describe a time you got a customer to think about their problem or need differently
- How do you decide what to include in your pitch?
- How do you know that you convinced a customer?
- Describe a time your sales pitch fell flat. How did you react?
- How do you adjust your sales pitch to different audiences?
Evaluation guidelines:
- Follows a structured process to identify key decision makers and their top priories
- Tailors a sales pitch to unique customer requirements
- Successfully transitions the relationship from supplier vendor to a partnership in achieving customer objectives.
Red flags:
- Sales pitch focuses on features and benefits
- Insights do not align with customer priorities
- Unable to articulate supplier differentiators
- Can’t adjust mid-pitch
Competency: Drives two-way communication
Definition:
- Clearly articulates the supplier’s value proposition and engages the customer in addressing business priorities
- Reads nonverbal cues and identifies unanticipated customer needs
- Coordinates and secures buy-in from internal stakeholders
Sample interview questions:
- How would you describe your typical relationship with a customer?
- How do you get customers to talk about their business priorities?
- What nonverbal cues do you look for during sales interactions?
- Describe a time when you proactively addressed an unstated customer need.
- How do you handle gatekeepers to gain access to busy executives?
- Discuss a time when you overcame difficulty in coordinating across functions.
Evaluation guidelines:
- Relationships are based on seller’s ability to teach customer pain points
- Modifies behavior based on nonverbal cues
- Relays stories of successfully coordinating across silos in response to complex customer needs
Red flags:
- Does not seem open and or approachable.
- Inflexible
- Likes to have the last word
- Cannot read body language
- Struggles to balance multiple relationships
Competency: Knows customer value drivers
Definition:
- Knows the customer’s business deeply and can discuss issues from multiple angles.
- Is comfortable talking to a wide range of decision influencers.
- Successfully links supplier capabilities to individual goals to overcome barriers to purchase.
Sample interview questions
- What process do you follow to gain buy in from customer stakeholders?
- How do you identify key decision makers and influencers?
- How do you decide what is and is not important to the decision-maker?
- Describe your process for researching the customer’s business.
- How do you track potential competitor advocates within customer organizations?
- Describe a time when your offerings did not match the customer’s needs.
Evaluation guidelines
- Follows a structured process to identify key decision makers and their top priorities
- Tailors the sales pitch to unique customer requirements
- Successfully transitions the relationship from supplier vendor to a partnership built around achieving customer objectives
Red flags
- Unaware of all parties involved in the deal.
- Uses the same pitch for everyone.
- Views relationships transactionally.
- Unclear on customers’ business priorities.
Competency: Can identify economic drivers
Definition:
- Keenly tracks economic and industry activity and understands its implications on customer business, including potential new business opportunities.
- Educates customers on industry trends and best practices adopted by peer companies.
Sample interview questions
- Talk about a time when you successfully pushed through a price increase.
- What is your response to customers demanding pricing concessions?
- What is your reaction to a competitor who consistently undercuts your prices?
- Describe a time when you successfully negotiated on unclear price guidelines.
- Describe a time when you walked away from a deal because of price.
Evaluation guidelines
- Comfortable talking about price at any stage of the sales cycle and does not depend on absolute pricing guidelines
- Gets customers to see beyond price and appreciate the supplier’s unique differentiators
- Relays a history of closing deals with customers at a significant profit
Red flags
- Cannot clearly justify price with value
- Unaware of customers purchasing ability
- Frequently concedes on pricing and discounts
Competency: Can pressure the customer
Definition:
- Understands the decision-making process and has the ability to influence key decision makers.
- Preempts stakeholder objections and pushes the customer to a favorable outcome.
- Develops customer advocates who sell and build consensus on the supplier’s behalf.
Sample interview questions
- What is the one thing customers would associate with or say about you?
- How do you build consensus among everyone involved in a sale?
- Describe an instance where you manage to progress a stalled deal.
- How have you dealt with customers annoyed by your negotiation tactics?
- Describe a time you compromise to close a deal. What did you offer?
- Discuss a time you convinced a customer advocate to sell on your behalf.
Evaluation guidelines
- Is a skilled negotiator who understands the decision-making process and the priorities of different stakeholders
- Generates consensus among stakeholders and independently closes deals
- Primarily targets advocates rather than senior-most stakeholders to secure buy in
Red flags
- Overly aggressive or passive with customers
- Finds it hard to build stakeholder consensus
- Exercises price concessions to end negotiations
- Focuses exclusively on senior-most contacts






